
Straight-line depreciation determines a depreciation expense, that you will pay in equal annual instalments until the entire asset is depreciated to its salvage value. This method often is used if an asset is expected to lose greater value or have greater utility in earlier years. Some companies may use the double-declining balance equation for more aggressive depreciation and early expense management. An asset account which is expected to have a credit balance (which is contrary to the normal debit balance of an asset account). For example, the contra asset account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is related to Accounts Receivable. The contra asset account Accumulated Depreciation is related to a constructed asset(s), and the contra asset account Accumulated bookkeeping Depletion is related to natural resources.
Declining Balance Method
When you have a fixed asset like a vehicle, building, or piece of equipment, these things will naturally suffer some wear and tear over time. Depreciation measures the economic effect of this wear and tear and allows you to allocate that change in value over the asset’s usable life. Tax depreciation follows a system called MACRS, which stands for modified accelerated cost recovery system. MACRS is a form of accelerated depreciation, and the IRS publishes tables for each type of property. Work with your accountant to be sure you’re recording the correct depreciation for your tax return.

Types of Depreciation for Book Purposes (GAAP) With Examples
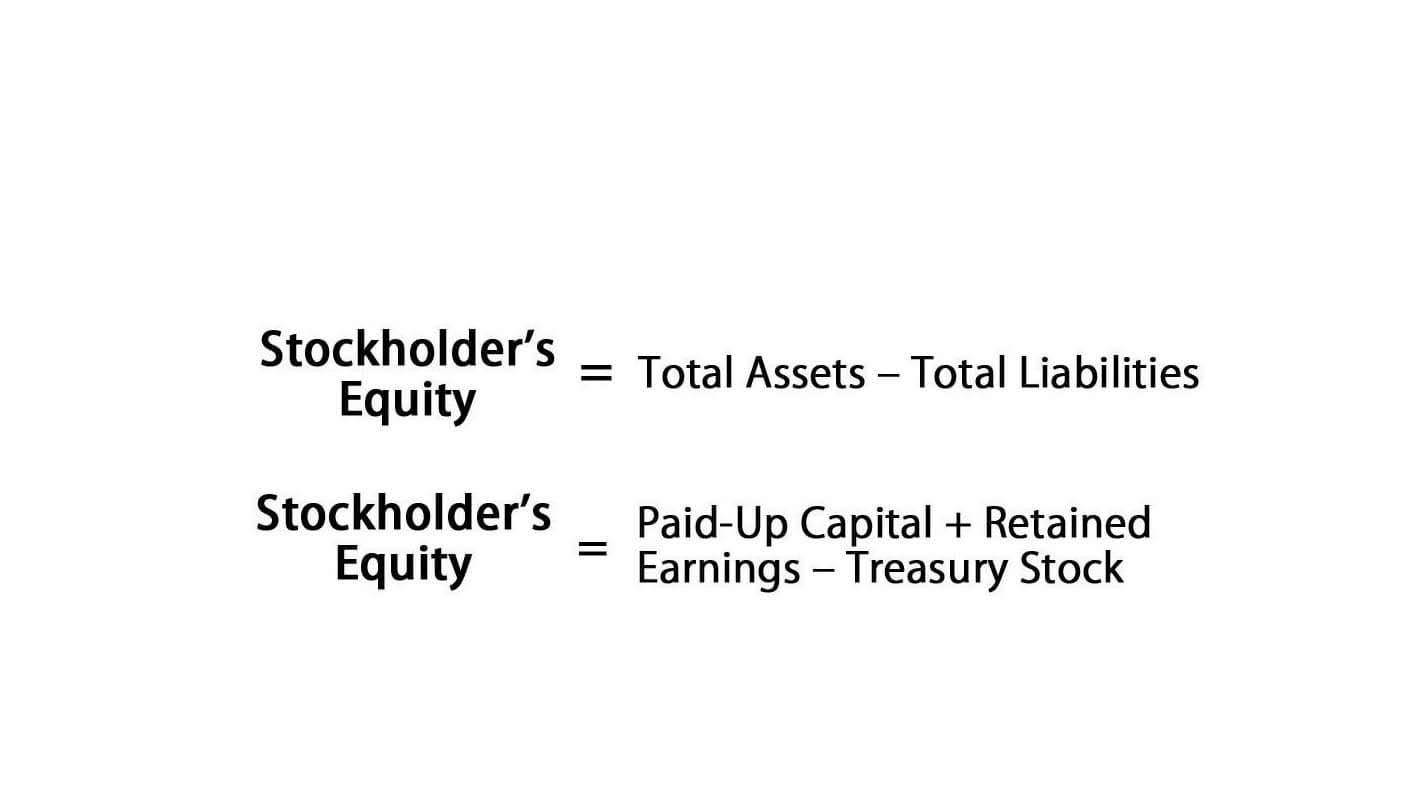
This formula is best for small businesses seeking a simple method of depreciation. A company estimates an asset’s useful life and salvage value (scrap value) at the end of its life. Depreciation determined Insurance Accounting by this method must be expensed in each year of the asset’s estimated lifespan. A record in the general ledger that is used to collect and store similar information.
- Let’s understand this by continuing the example of server purchase earlier.
- If a company has losses in a particular period, it can carry those losses forward to offset future taxable profits.
- The part of the cost that is charged to operation during an accounting period is known as depreciation.
- A patent, for example, is an intangible asset that a business can use to generate revenue.
- Every kind of asset your company owns can be bought or sold, used or discarded.
- Depreciation ensures that a company’s financial statements reflect the true value of its assets over time.
- Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox.Part of the business.com network.
What is the Depreciation Rate for Fixed Assets?
- Let’s say you want to find the van’s depreciation expense in the first, second, and third year you own it.
- Some assets like buildings tend to wear and tear at a steady rate, and are measured with formulas like the straight-line method.
- The machine has a salvage value of R3,000, a depreciable base of R27,000, and a five-year useful life.
- To demonstrate this, let’s assume that a retailer purchases a $70,000 truck on the first day of the current year, but the truck is expected to be used for seven years.
- By subtracting deferred revenue from deferred expenses, a company can determine the amount of deferred assets that it has.
- Accelerated depreciation methods, such as the double-declining balance method, generate more depreciation expenses in the early years of an asset’s life.
- You’ll need to understand how depreciation impacts your financial statements.
Overall, deferred tax assets can be an important source of tax depreciable assets relief for companies. However, it is important to carefully consider the conditions for recognizing deferred tax assets and to create a valuation allowance if necessary. Deferred tax assets are tax assets that will be realized in future periods. They arise when a company has overpaid taxes or has tax credits that can be used to offset future tax liabilities. Deferred tax assets can also be created when a company has losses that can be carried forward to offset future taxable profits. A company may receive payment for a good or service before it has provided the good or service.
Depreciation Not Based on Years
- In this article, you will get to know the importance of the calculation of Depreciation in detail.
- Depreciation is an accounting method that companies use to apportion the cost of capital investments with long lives, such as real estate and machinery.
- It also does not factor in the accelerated loss of an asset’s value in the short term or the likelihood that maintenance costs will go up as the asset gets older.
- In this example, we can say that the service given by the weighing machine in its first year of life was $200 ($1,000 — $800) to the company.
That said, if losses are recorded on such a property whereby the loss is ordinary, it is fully deductible against the income. Internal Revenue Code defines depreciable or real business assets held for over one year as Section 1231 property. The gain earned from the sale of such assets is subject to taxation at the lower capital gains tax rate against the rate applicable to ordinary income.



Leave a reply